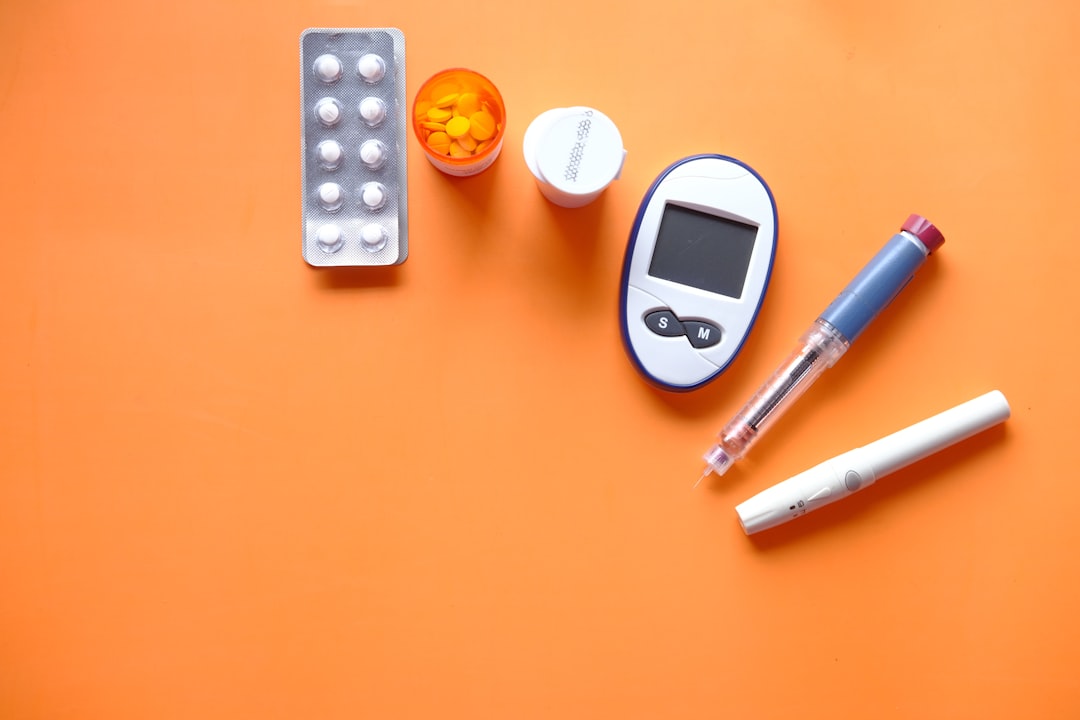
Non-invasive diabetes monitoring devices are innovative technologies that allow individuals with diabetes to monitor their blood glucose levels without the need for traditional invasive methods such as finger pricking. These devices use advanced technology to measure glucose levels through the skin, making it a more convenient and less painful option for diabetes patients. Monitoring blood glucose levels is crucial for individuals with diabetes as it helps them manage their condition effectively and prevent complications.
Key Takeaways
- Non-invasive diabetes monitoring devices are becoming increasingly popular as an alternative to traditional invasive methods.
- The need for non-invasive monitoring devices is driven by the desire to reduce patient discomfort and improve compliance with monitoring protocols.
- Current challenges in diabetes monitoring include the need for frequent testing, the invasiveness of traditional methods, and the cost of monitoring devices.
- Non-invasive diabetes monitoring devices work by measuring glucose levels through the skin or other non-invasive means.
- Advantages of non-invasive diabetes monitoring devices include improved patient comfort, increased compliance with monitoring protocols, and potentially lower costs.
The Need for Non-Invasive Diabetes Monitoring Devices
Traditional blood glucose monitoring methods, such as finger pricking, can be challenging for many diabetes patients. The constant need to draw blood multiple times a day can be painful and uncomfortable, leading to non-compliance and reluctance to monitor glucose levels regularly. Additionally, these methods can be inconvenient, requiring individuals to carry around monitoring equipment and find a private space to perform the test.
There is a clear need for a less invasive and more convenient monitoring method that can encourage regular monitoring and improve patient compliance. Non-invasive diabetes monitoring devices offer a solution to these challenges by providing a pain-free and hassle-free way to monitor blood glucose levels.
Current Challenges in Diabetes Monitoring
Traditional monitoring methods come with several challenges that can impact the accuracy and convenience of monitoring blood glucose levels. One of the main challenges is the pain and discomfort associated with finger pricking. Many individuals find it difficult to prick their fingers multiple times a day, leading to non-compliance and inadequate monitoring.
In addition to pain and discomfort, traditional monitoring methods can also be inaccurate due to various factors such as improper technique, environmental conditions, or interference from substances on the skin. This can lead to incorrect readings and mismanagement of diabetes.
Furthermore, carrying around monitoring equipment can be inconvenient for individuals with diabetes, especially when they are on the go or traveling. The need to have access to a private space and carry supplies can be burdensome and may discourage regular monitoring.
How Non-Invasive Diabetes Monitoring Devices Work
| Device Type | How it Works | Accuracy | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) | A small sensor is inserted under the skin to measure glucose levels in the interstitial fluid. The sensor sends data to a receiver or smartphone app. | Highly accurate | Expensive |
| Flash Glucose Monitoring | A small sensor is inserted under the skin to measure glucose levels in the interstitial fluid. The sensor can be scanned with a reader or smartphone app to display glucose readings. | Highly accurate | Expensive |
| Non-Invasive Glucose Monitoring | Uses infrared light to measure glucose levels in the blood vessels near the skin surface. Some devices require a finger prick to calibrate the device. | Less accurate than invasive methods | Varies depending on device |
Non-invasive diabetes monitoring devices use advanced technology to measure glucose levels through the skin without the need for invasive methods. One common technology used is near-infrared spectroscopy, which measures the absorption of light by glucose molecules in the skin. This information is then used to calculate blood glucose levels.
Another technology used is transdermal extraction, which involves the use of a patch or sensor that is placed on the skin. The patch or sensor contains tiny needles or microneedles that penetrate the skin and extract interstitial fluid, which is then analyzed for glucose levels.
Compared to traditional monitoring methods, non-invasive devices offer a more convenient and pain-free option for individuals with diabetes. They eliminate the need for finger pricking and provide a more comfortable experience for patients.
Advantages of Non-Invasive Diabetes Monitoring Devices
Non-invasive diabetes monitoring devices offer several advantages over traditional monitoring methods. One of the main advantages is the reduction in pain and discomfort for patients. By eliminating the need for finger pricking, individuals with diabetes can monitor their blood glucose levels without experiencing pain or discomfort, leading to improved compliance and regular monitoring.
In addition to pain reduction, non-invasive devices also provide more accurate readings compared to traditional methods. By using advanced technology to measure glucose levels through the skin, these devices can provide more reliable and consistent results, allowing individuals to make informed decisions about their diabetes management.
Furthermore, non-invasive devices offer convenience and ease of use. They eliminate the need to carry around monitoring equipment and find a private space to perform the test. Individuals can simply wear a patch or sensor and have continuous access to their glucose readings throughout the day.
Examples of Non-Invasive Diabetes Monitoring Devices
There are several non-invasive diabetes monitoring devices available on the market today. One popular device is the continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) system, which uses a sensor inserted under the skin to measure glucose levels in the interstitial fluid. The sensor sends real-time glucose readings to a receiver or smartphone app, allowing individuals to monitor their levels throughout the day.
Another example is the optical glucose monitoring device, which uses near-infrared spectroscopy to measure glucose levels through the skin. This device typically consists of a handheld device or a wearable patch that individuals can use to measure their glucose levels without the need for finger pricking.
Clinical Studies and Results of Non-Invasive Diabetes Monitoring Devices
Numerous clinical studies have been conducted to evaluate the effectiveness and accuracy of non-invasive diabetes monitoring devices. These studies have consistently shown that non-invasive devices provide reliable and accurate glucose readings, comparable to traditional invasive methods.
For example, a study published in the Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology compared the accuracy of a non-invasive CGM system with traditional finger pricking. The study found that the non-invasive CGM system provided glucose readings within 10% of the reference values, demonstrating its accuracy and reliability.
Another study published in Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics evaluated the performance of an optical glucose monitoring device. The study found that the device provided accurate glucose readings and was well-tolerated by individuals with diabetes.
Future of Non-Invasive Diabetes Monitoring Devices
The future of non-invasive diabetes monitoring devices looks promising, with potential advancements in technology on the horizon. Researchers are continuously working on improving the accuracy and reliability of these devices, as well as exploring new technologies that can further enhance monitoring capabilities.
One potential advancement is the integration of non-invasive monitoring devices with other health monitoring devices. For example, researchers are exploring the possibility of combining non-invasive glucose monitoring with wearable fitness trackers or smartwatches. This integration would allow individuals to monitor their glucose levels alongside other health metrics, providing a comprehensive view of their overall health.
Cost and Accessibility of Non-Invasive Diabetes Monitoring Devices
The cost of non-invasive diabetes monitoring devices can vary depending on the brand and features of the device. However, in general, these devices tend to be more expensive than traditional monitoring methods. This cost can be a barrier for some individuals, especially those with limited financial resources.
However, it is important to consider the long-term benefits and potential cost savings associated with non-invasive devices. Regular monitoring and effective management of diabetes can help prevent complications and reduce healthcare costs in the long run. Additionally, as technology advances and more companies enter the market, the cost of these devices is expected to decrease, making them more accessible to a wider range of patients.
The Impact of Non-Invasive Diabetes Monitoring Devices on Patient Care
Non-invasive diabetes monitoring devices have the potential to revolutionize patient care for individuals with diabetes. By providing a pain-free and convenient way to monitor blood glucose levels, these devices can improve patient compliance and encourage regular monitoring. The accuracy and reliability of non-invasive devices also ensure that individuals can make informed decisions about their diabetes management.
Incorporating non-invasive monitoring devices into diabetes patient care can lead to improved patient outcomes and quality of life. Regular monitoring allows individuals to identify trends and patterns in their glucose levels, enabling them to make necessary adjustments to their diet, medication, or lifestyle. This proactive approach to diabetes management can help prevent complications and ensure better overall health for individuals with diabetes.
As technology continues to advance and more research is conducted in this field, non-invasive diabetes monitoring devices are expected to become even more accurate, convenient, and accessible. The future looks promising for individuals with diabetes as they embrace these innovative technologies to manage their condition effectively.
If you’re interested in the latest advancements in non-invasive diabetes monitoring devices, you won’t want to miss this breakthrough article. In a world where managing diabetes can be a daily challenge, researchers have made significant progress in developing innovative technologies that eliminate the need for painful finger pricks. This article explores how these cutting-edge devices work and the potential impact they could have on the lives of millions living with diabetes. To learn more about this exciting development, check out the article on Tablet Jankari’s website: Breakthrough in Non-Invasive Diabetes Monitoring Devices.
FAQs
What is the article about?
The article is about a breakthrough in non-invasive diabetes monitoring devices.
What is diabetes?
Diabetes is a chronic disease that affects how your body processes blood sugar (glucose).
What are the current methods of monitoring diabetes?
The current methods of monitoring diabetes include blood glucose meters, continuous glucose monitoring systems, and A1C tests.
What are the limitations of current diabetes monitoring methods?
The limitations of current diabetes monitoring methods include the need for frequent blood glucose testing, discomfort associated with finger pricks, and the cost of continuous glucose monitoring systems.
What is the new non-invasive diabetes monitoring device?
The new non-invasive diabetes monitoring device is a wearable sensor that measures glucose levels in sweat.
How does the new non-invasive diabetes monitoring device work?
The new non-invasive diabetes monitoring device works by using a small electrical current to stimulate the sweat glands and measure the glucose levels in the sweat.
What are the benefits of the new non-invasive diabetes monitoring device?
The benefits of the new non-invasive diabetes monitoring device include non-invasive testing, reduced discomfort, and potentially lower costs.
When will the new non-invasive diabetes monitoring device be available?
The availability of the new non-invasive diabetes monitoring device is not yet known as it is still in the development stage.